Robotic Surgery - Homepage
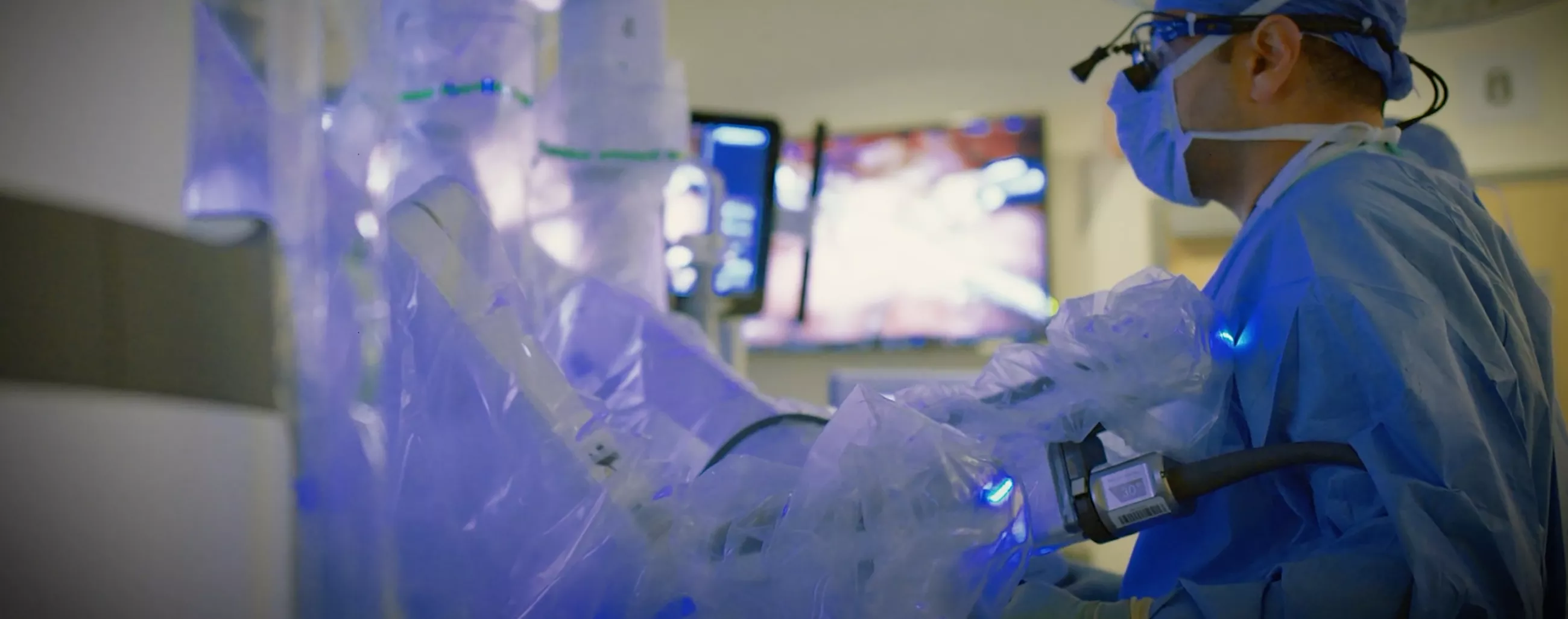




The Department of Surgery at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is at the forefront of utilizing advanced robotic technology to perform a wide range of surgical procedures. With a commitment to innovation and patient-centered care, UCSF has embraced robotic-assisted surgery as a means to provide patients with minimally invasive techniques, improved outcomes, and faster recovery times.
Here are some of the key robotic procedures performed at UCSF, including Xi procedures, SP procedures, and robotic lung nodule biopsies (robotic bronchoscopy).
Our mission is to develop the next generation of leaders in academic surgery.
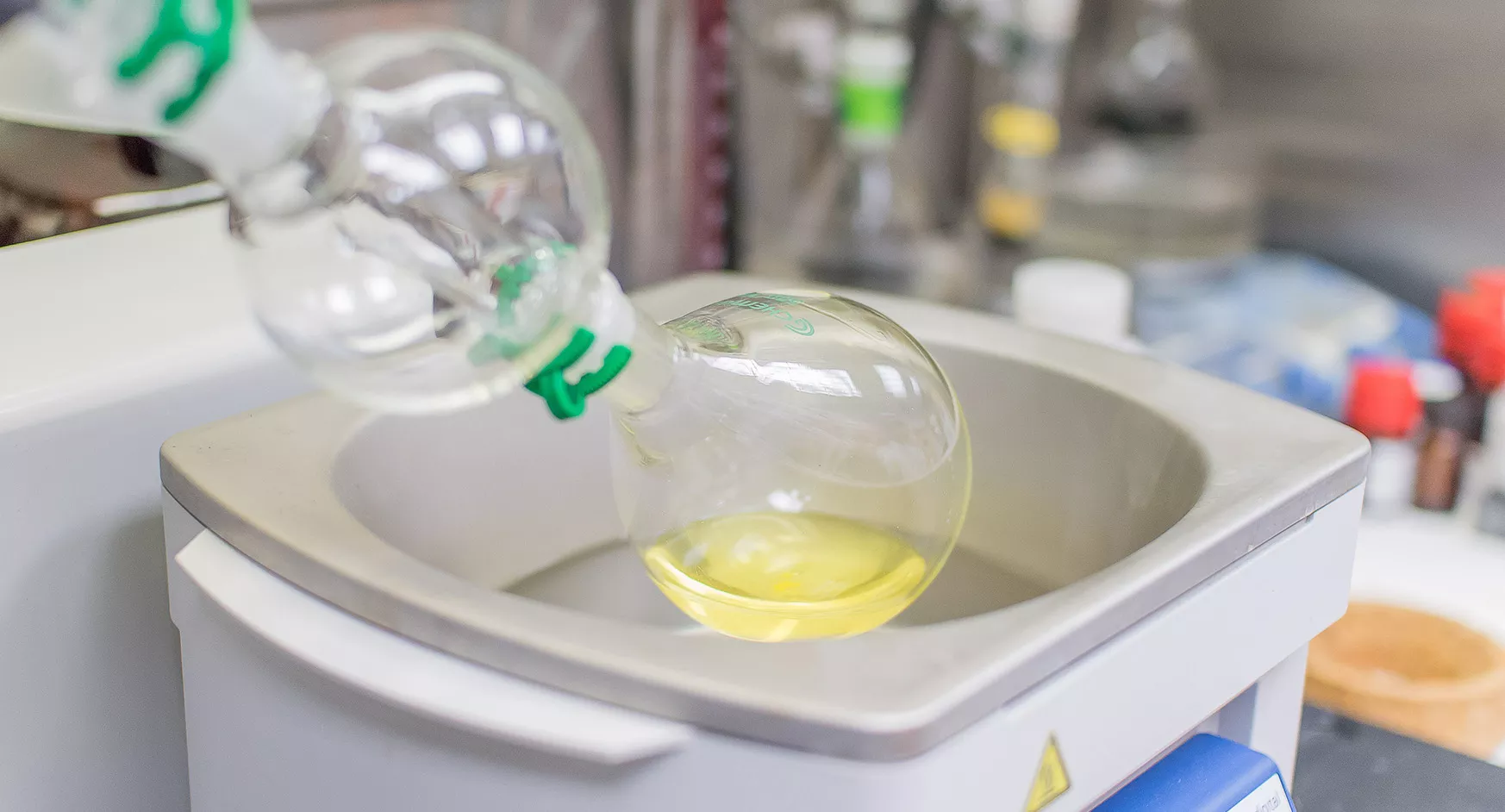

Research & Innovations
The UCSF Robotic Surgery Program stands at the forefront of pioneering advancements in medical research. With a strong focus on various areas of study, ranging from cancer Research to clinical trials, translational, biomechanical, and bench research, we are committed to making significant contributions and transforming healthcare.
UCSF Thoracic Surgery – At the Forefront of Medical and Surgical Innovation
UCSF Minimally Invasive and Robotic Thoracic Surgery stands at the forefront of surgical innovation, leveraging its strategic location in Silicon Valley to collaborate with industry leaders and bring the latest technological advancements to its patients. Discover the groundbreaking advancements in robotic surgery at UCSF, where innovation meets precision to redefine patient care.
Related websites:
UCSF Thoracic Surgery
Featured surgeons: Dr. Johannes Kratz, Dr. Diana Yu, Dr. Stanley Rogers, and Dr. Jasleen Kukreja
Featured UCSF programs: Minimally Invasive and Robotic Thoracic Surgery, Lung Transplant Program.